Scenario Planning: How to Future-Proof Your Financial Models Against Uncertainty
What is Scenario Planning in Finance?
Scenario planning is a strategic financial forecasting tool that helps organizations analyze multiple possible futures instead of relying on a single base case.
Rather than trying to predict exactly what will happen, scenario planning involves:
- Identifying key uncertainties that could affect your business
- Developing plausible narratives based on different combinations of those uncertainties
- Running financial models under each scenario to test resilience and flexibility
Unlike traditional forecasting, which assumes one most-likely future, scenario planning in finance embraces uncertainty by exploring outcomes from optimistic to pessimistic - and everything in between.
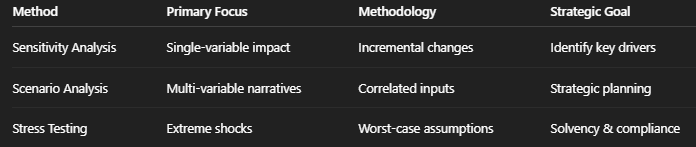
Scenario Analysis vs. Sensitivity Analysis vs. Stress Testing
Before building advanced scenario models, it’s critical to distinguish between the three core analytical techniques.
Scenario Analysis: Narrative-Driven, Multi-Variable Modeling
Scenario analysis evaluates multiple interdependent variables simultaneously to construct coherent future states. Examples include:
- A geopolitical supply-chain disruption
- A rapid AI-driven productivity boom
- A prolonged high-inflation environment
Rather than isolating variables, scenario analysis explores how inflation, interest rates, demand, labor costs, and capital markets interact under specific conditions. Its primary purpose is strategic flexibility, not precision forecasting.
Sensitivity Analysis: Identifying Key Financial Drivers
Sensitivity analysis isolates one variable at a time, holding all others constant. For example:
- What happens to EBITDA if prices increase by 5%?
- How sensitive is cash flow to customer churn?
This approach is ideal for identifying key value drivers - the assumptions that matter most. By focusing data accuracy and management attention on high-impact variables, organizations often improve forecast accuracy by up to 30%.
Stress Testing: Survival Under Extreme Conditions
Stress testing models low-probability, high-impact events, such as:
- A sudden 10%+ equity market crash
- Severe liquidity freezes
- Systemic financial shocks
While scenario analysis emphasizes plausibility, stress testing focuses on solvency and regulatory compliance, particularly in banking and financial services.
Key Principles of Scenario Planning
- Multiple Futures – Accept that the future is uncertain and explore a range of outcomes.
- Plausibility and Coherence – Scenarios must be realistic and internally consistent.
- Focus on Key Uncertainties – Prioritize the biggest financial and operational risks.
- Decision-Oriented – The goal is not prediction, but better decision-making today.
Why is Scenario Planning Crucial for Financial Models?
Incorporating scenario planning into financial forecasting offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Risk Management – Identify hidden risks and vulnerabilities.
- Improved Strategic Decision-Making – Evaluate the impact of different strategies in varied conditions.
- More Realistic Forecasts – See a range of potential outcomes instead of one static projection.
- Stronger Stakeholder Confidence – Stress-test assumptions to prove models are resilient.
- Better Communication – Encourage richer discussions on financial risks and opportunities.
Building Scenarios into Your Financial Models: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Identify Key Uncertainties
Brainstorm critical factors that could impact your financial models:
- Macroeconomic: interest rates, inflation, GDP growth
- Industry Trends: technological disruption, regulation
- Company-Specific: sales growth, customer demand, supply costs
Step 2: Select Scenario Drivers
Choose 2–3 of the most impactful, independent variables to avoid complexity.
Step 3: Define Scenario Narratives
Develop clear storylines for each case:
- Best Case (Optimistic): favorable market and growth conditions
- Base Case (Expected): business as usual
- Worst Case (Pessimistic): downturn or operational challenges
Other variations may include:
- Technological Disruption: Rapid adoption of a new technology
- Regulatory Shift: New laws impacting your industry
- Economic Recession: A downturn in the economy
Step 4: Quantify Assumptions
Translate narratives into financial model inputs, such as:
- Adjusting sales growth projections
- Modifying cost assumptions
- Changing discount rates for interest rate volatility
Step 5: Run the Financial Models
Test each scenario’s impact on:
- Revenue
- Profitability
- Cash flow
- Valuation
Step 6: Analyze Results
Compare the financial outputs across different scenarios. Look for:
- Key Sensitivities: Which variables have the biggest impact on results?
- Break-Even Points: At what point does the project become unprofitable?
- Risks and Opportunities: What are the potential downsides and upsides?
Step 7: Develop Contingency Plans
Based on your scenario analysis, create contingency plans for each scenario. For example:
- Best Case: plan for scaling operations to meet increased demand
- Worst Case: prepare cost-cutting measures or alternative revenue streams.
Step 8: Regularly Review
Scenario planning is not one-and-done. Revisit and update scenarios as markets, regulations, or customer behavior evolve.
Real-World Examples of Scenario Planning in Finance
Retail Company
- Drivers: economic growth (strong vs. recession) and online adoption.
- Outputs: sales forecasts, profitability by channel.
- Decisions: store expansion vs. e-commerce investment.
Technology Startup
- Drivers: adoption rate of new tech and competitive landscape.
- Outputs: revenue projections, funding needs, valuation.
- Decisions: fundraising strategy and product development priorities.
Manufacturing Company
- Drivers: raw material prices and product demand.
- Outputs: production costs, cash flow, profitability.
- Decisions: pricing strategies, sourcing, capacity planning.
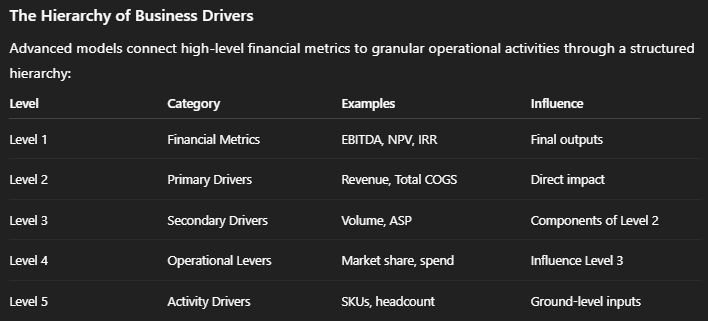
The Architecture of Driver-Based Financial Models
What Is Driver-Based Planning?
Driver-based planning structures financial models around the variables that actually cause financial outcomes, rather than projecting financial statements in isolation.
A driver is an independent variable—such as churn rate, production volume, pricing, or headcount—that cascades through the model and shapes results.
Categories of Key Drivers
- Macroeconomic drivers: Inflation, interest rates, FX, GDP growth
- Operational drivers: Pricing, churn, CAC, COGS, headcount
- Industry-specific drivers:
- SaaS: MRR, churn, expansion revenue
- Manufacturing: Unit costs, throughput, capacity
Identifying the right drivers requires deep collaboration between finance and operating teams and validation against historical data.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Scenario Planning
- Creating too many scenarios (analysis paralysis)
- Using unrealistic assumptions
- Treating scenarios as predictions instead of planning tools
- Failing to revisit and update scenarios regularly
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How is scenario planning different from financial forecasting?
A: Forecasting usually assumes one most likely case, while scenario planning explores multiple plausible futures.
Q: How often should businesses update scenarios?
A: At least annually - more frequently in volatile industries such as tech, retail, or energy which may be monthly or quarterly.
Q: What industries benefit most from scenario planning?
A: Finance, retail, technology, energy, and manufacturing - all sectors exposed to high uncertainty.
Q: Can scenario planning help startups?
A: Yes. For startups, scenario planning is critical for investment decisions, fundraising, and managing runway.


