Applying the McKinsey 7S Model to Your Finance Strategy: A Blueprint for Alignment
Introduction: Why Finance Strategies Fail Without Alignment
Is your finance strategy delivering results — or do your teams, systems, and processes feel misaligned? Many finance leaders focus heavily on strategy while overlooking the softer, cultural elements that actually drive long-term performance.
That’s where the McKinsey 7S Model comes in.
Originally developed for large corporations, this framework is just as powerful for finance firms of all sizes. By analyzing seven interdependent elements, you can identify gaps, resolve inconsistencies, and align every part of your business for stronger results.
The McKinsey 7S Model: An Overview
The model rests on one key idea: an organization’s success depends on the alignment of seven interconnected elements — all beginning with S.
These are split into Hard and Soft elements:
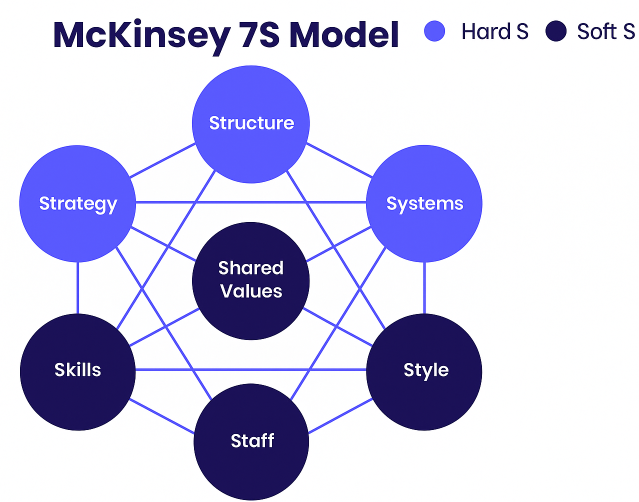
Hard Elements (Tangible and Directly Managed)
Hard elements are easier to define and directly influence through processes and policies.
| Element | Definition | Finance Application |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy | The plan for achieving success and competitive advantage. | Your finance business plan: focus areas (wealth management, FinTech), differentiation, and competitive positioning. |
| Structure | How the company organizes roles, hierarchy, and decision-making. | Team setup (compliance, sales, research), reporting lines, and centralized vs. decentralized decision-making. |
| Systems | The processes and tools that support daily operations. | Trading platforms, CRM tools, compliance protocols, budgeting, and reporting systems. |
Soft Elements (Intangible and Culture-Driven)
Soft elements are harder to measure but critical for shaping performance and long-term alignment.
| Element | Definition | Finance Application |
|---|---|---|
| Shared Values | The cultural core that influences all decisions. | Values like fiduciary duty, client trust, and innovation. |
| Skills | The organization’s collective capabilities. | Risk modeling, algorithmic trading, or niche expertise in areas like M&A. |
| Style | Leadership approach and management behaviors. | Hands-on style for compliance-heavy firms vs. empowering style for innovation teams. |
| Staff | Talent management, hiring, and retention. | Recruiting skilled advisors and creating growth programs to retain top analysts. |
A 7-Step Process to Apply the Model in Finance
The power of the 7S Model lies in its ability to spot misalignments before they hinder growth. Here’s how to use it for your finance strategy:
- Analyze Each Component
Start with Shared Values, then move through Hard and Soft elements. Ask: Does our structure support our strategy? Do we have the skills to achieve our goals? - Identify Gaps and Inconsistencies
Example: If your strategy focuses on international growth but your systems lack cross-border compliance processes, that’s a gap. - Define the Desired State
For each S, ask: What needs to change for us to execute effectively? Align this vision with long-term business goals. - Build a Change Management Plan
Translate analysis into action. Define KPIs, assign ownership, and set milestones. - Execute with Discipline
Whether it’s rolling out a new CRM or launching a staff training program, execution drives real impact. - Monitor Progress
Track performance regularly against KPIs. Use dashboards to visualize alignment across teams. - Adapt and Refine
Finance markets change fast. Use new data, regulatory updates, and client feedback to refine your model continuously.
Benefits and Limitations of the 7S Model
Key Benefits:
- Helps finance firms visualize how internal elements connect.
- Simplifies planning for change initiatives.
- Improves cross-team alignment during mergers, restructuring, or expansion.
Limitations to Consider:
- Requires in-depth analysis and benchmarking.
- Focuses internally — doesn’t account for external market shifts.
- Time-intensive if not paired with clear execution plans.
FAQs About the McKinsey 7S Model in Finance
Q: What is the main purpose of the McKinsey 7S Model?
A: The model helps organizations achieve alignment between strategy, systems, staff, and culture to improve overall performance.
Q: How is the McKinsey 7S Model relevant to finance firms?
A: Finance firms face strict compliance requirements, fast-changing markets, and high client expectations. The 7S framework ensures that strategic plans, risk controls, and staff capabilities all work together.
Q: What’s the difference between Hard and Soft elements?
A: Hard elements (strategy, structure, systems) are tangible and easier to manage. Soft elements (skills, staff, style, shared values) are cultural and harder to measure but crucial for long-term success.
Q: Can small finance firms use the 7S Model?
A: Yes — in fact, small firms benefit greatly. Even with lean teams, the model helps prevent misalignments that could hinder growth.
Q: What’s an example of misalignment in finance?
A: If a firm’s strategy emphasizes client trust but leadership style prioritizes aggressive sales targets, this conflict creates cultural misalignment and client dissatisfaction.
Making Your Finance Strategy Work Like a Machine
The McKinsey 7S Model is more than a framework — it’s a practical blueprint for alignment. By applying it to your finance strategy, you can ensure that people, processes, and culture all move in the same direction.
Start today by mapping your seven elements. You’ll be surprised at how quickly hidden gaps become clear — and how much smoother your finance strategy runs once they’re aligned.

